#64 Adaptations of the leaf, stem and root
to different environments
Plants which live in extreme environments have adaptations to control their transpiration rate. Most modifications are adaptations to very dry (arid) environments. Water plants have no problem of water shortage. They do not need adaptations to conserve water as desert plants.
Plants modified to cope with a lack of water are called xerophytes. Living in deserts where water is scarce and evaporation is rapid, or in windy habitats where evaporation can also be rapid, they have to cut down water loss.
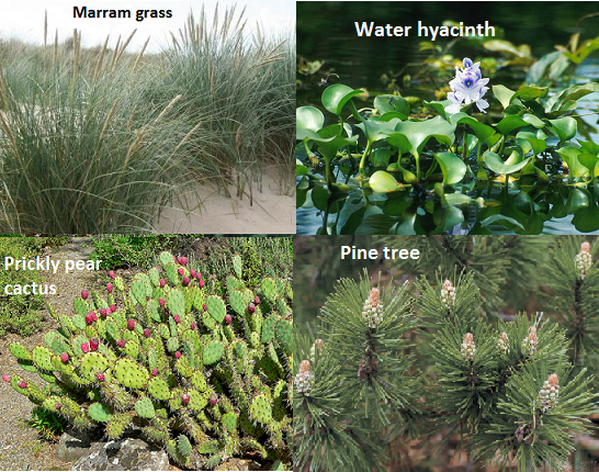
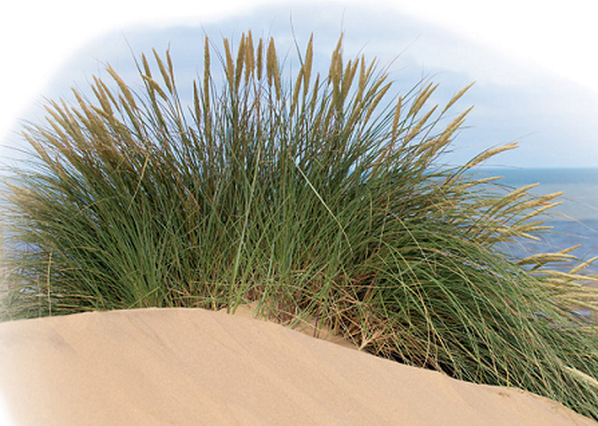
1. Marram grass (Ammophila)
1. Marram grass (Ammophila)
- Very long roots to search for water deep down in sand dunes.
- Leaves that roll up in dry weather to increase humidity around stomata, reducing transpiration.
- Sunken stomata to create high humidity and reduce transpiration.
- Fine hairs around stomata, reducing air movement so humidity builds up and transpiration is reduced.
2. Prickly pear cactus (Opuntia)
- Leaves reduced to spines – this reduces the surface area for transpiration and also acts as a defence against herbivores.
- Reduces number of stomata.
- Stomata cloesed during the day- when conditions for transpiration are most favourable.
- Fleshy stem - to store water.
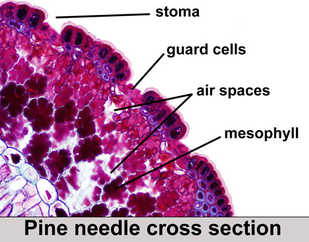
3. Pine tree (Pinus)
- Leaves needles-shaped to reduce surface area for transpiration and to resist wind damage.
- Sunken stomata to create high humidity and reduce transpiration.
- Thicsk waxy cuticle on the epidermis to prevent evaporation from leaf surface.
Water plants may have stomata on the tops of their leaves
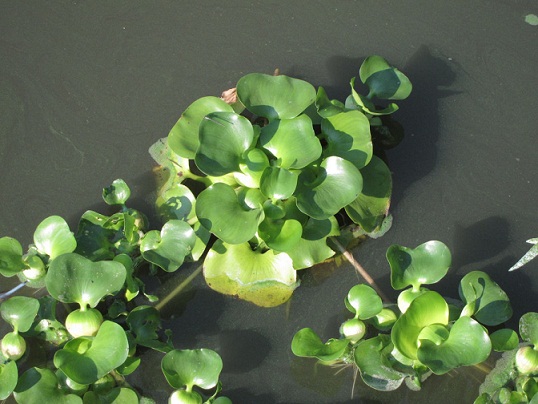
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia csassipes)
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia csassipes)
- Roots do not attach to to the bed of the river or pond where they grow, but just float freely in the water.
- The stems and leaf stalks have hollow spaces in them, filled with air à help to float on the top of the water where they can get plenty of light for photosynthesis.
- Leaves and stomata are on both surfaces, not just on the underside as in most plant à allow to absorb CO2 from the air, for photosynthesis.
- The cuticle on the upper and lower surfaces of the leaves is much thinner than in plants that don't live in water, there is no need to prevent water loss from the leaves.