# 61 Root hairs and water uptake by plants
Plants take in water from the soil, through their root hairs:
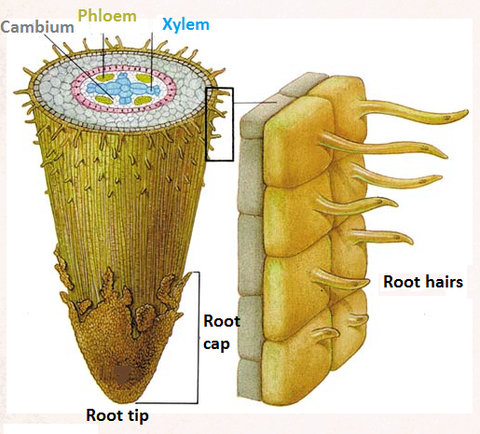
- At the very tip is a root cap. This is a layer of cells which protects the root as it grows through the soil.
- The rest of the root is covered by a layer of cells called the epidermis.
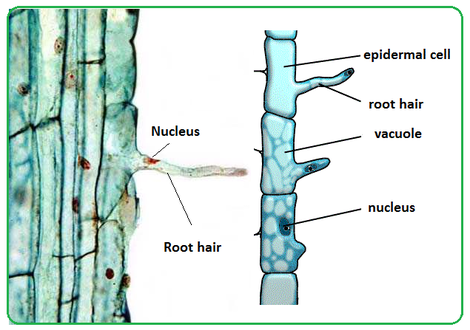
- The root hairs are a little way up from the root tip. Each root hair is a long epidermal cell. Root hairs do not live for very long. As the root grows, they are replaced by new ones.
Functions of root hair cells
- Increase the external surface area of the root for absorption of water and mineral ions (the hair increases the surface area of the cell to make it more efficient in absorbing materials).
- Provide anchorage for the plant.