# 65 Translocation of organic foods
in plants
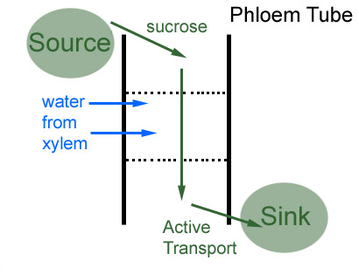
Translocation is the movement of organic food such sucrose and amino acids in phloem; from regions of production to regions of storage OR regions of utilisation in respiration or growth.
Carbohydrates are transported through a plant in the form of sucrose, glucose, and proteins as amino acids. Substances can be transported in any direction in phloem:
1. Glucose the product of photosynthesis is very important as it makes many other important nutrients, e.g. sucrose.
2. Amino acids are also transported in the phloem.
Sucrose and amino acids are transported to every tissue of the plant, each cell use it in a different way.
- from photosynthesising leaves down to roots for storage.
- upwards to growing buds, flowers, leaves and fruits for respiration and growth.
- from storage organs such as the root tubers to all parts of the plant.
1. Glucose the product of photosynthesis is very important as it makes many other important nutrients, e.g. sucrose.
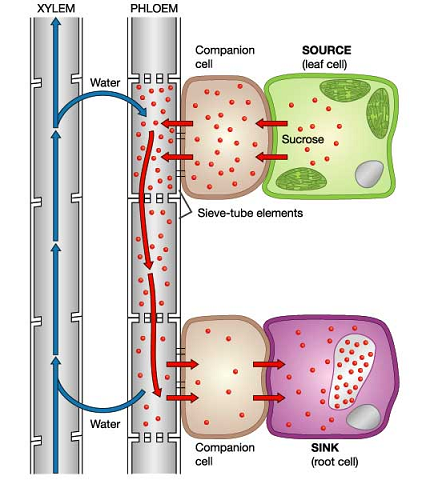
- Sucrose in the leaves then enters the phloem vessels.
- The phloem transports the sucrose all across the leaf where it can be made used of.
2. Amino acids are also transported in the phloem.
Sucrose and amino acids are transported to every tissue of the plant, each cell use it in a different way.
- Root cells convert sucrose into glucose for respiration and store it.
- Growing cells make cellulose for cell walls from sucrose and use the amino acids to make proteins for growth.
- And fruits use the sucrose to make the attractive scent and tasty nectar to attract insects.
The areas of the plant where sucrose is made, are called sources, and where they are delivered to and made use of are called sinks.
Ringing Experiment
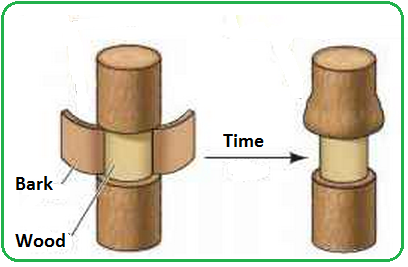
The phloem vessels are situated nearer to the bark in comparison with xylem à they can be selectively removed by cutting a ring in a stem just deep enough to cut the phloem but not the xylem.
Ringing Experiment
The phloem vessels are situated nearer to the bark in comparison with xylem à they can be selectively removed by cutting a ring in a stem just deep enough to cut the phloem but not the xylem.
After a week there is:
- a swelling above the ring
- reduced growth below the ring
- the leaves are unaffected.
Grey squirrels and other small mammals gnaw the bark and destroy the phloem that is in the inner bark region.